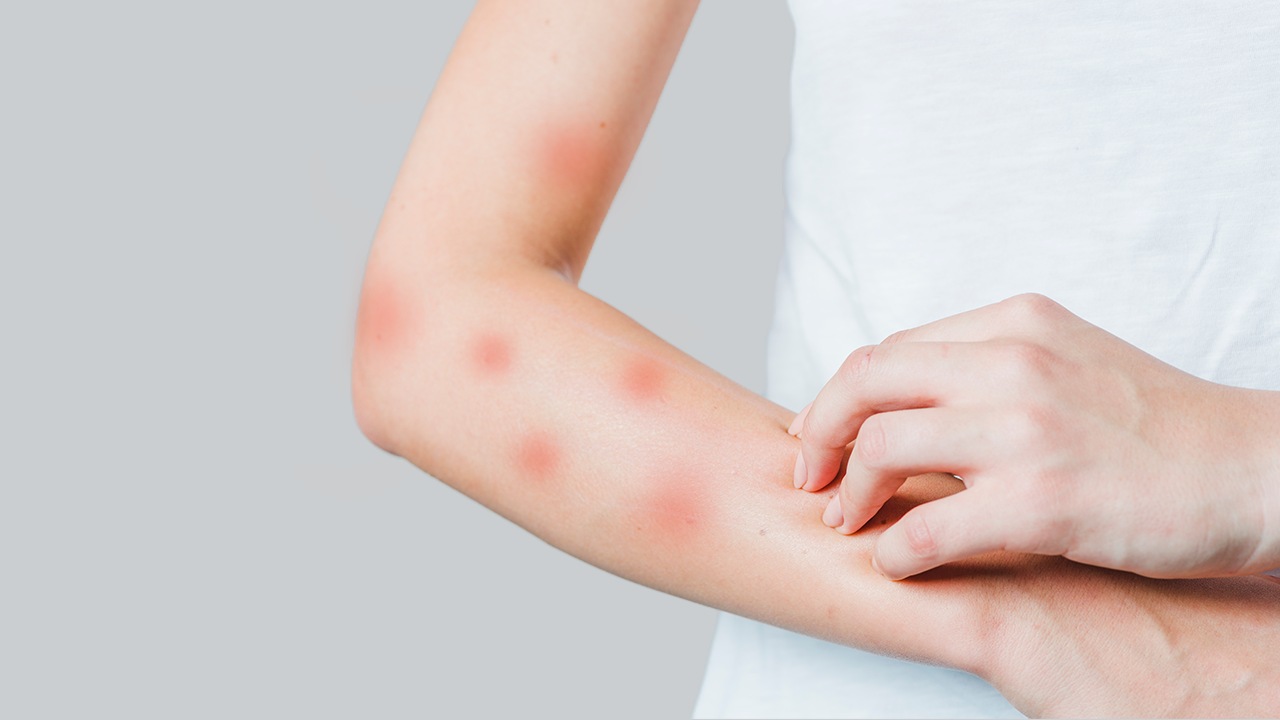
What Is an Allergy?
- Immune system overreaction
- When a person with an allergic constitution encounters an allergen, the allergic antibody in the body reacts with the allergen and releases histamine, which causes inflammatory reaction and allergic symptoms.
- The most common allergic symptoms are itchy nose, itchy eyes, red skin, swollen throat, diarrhea, etc. Allergic diseases include allergic rhinitis, asthma, ectopic dermatitis, etc.
Type I
|
|
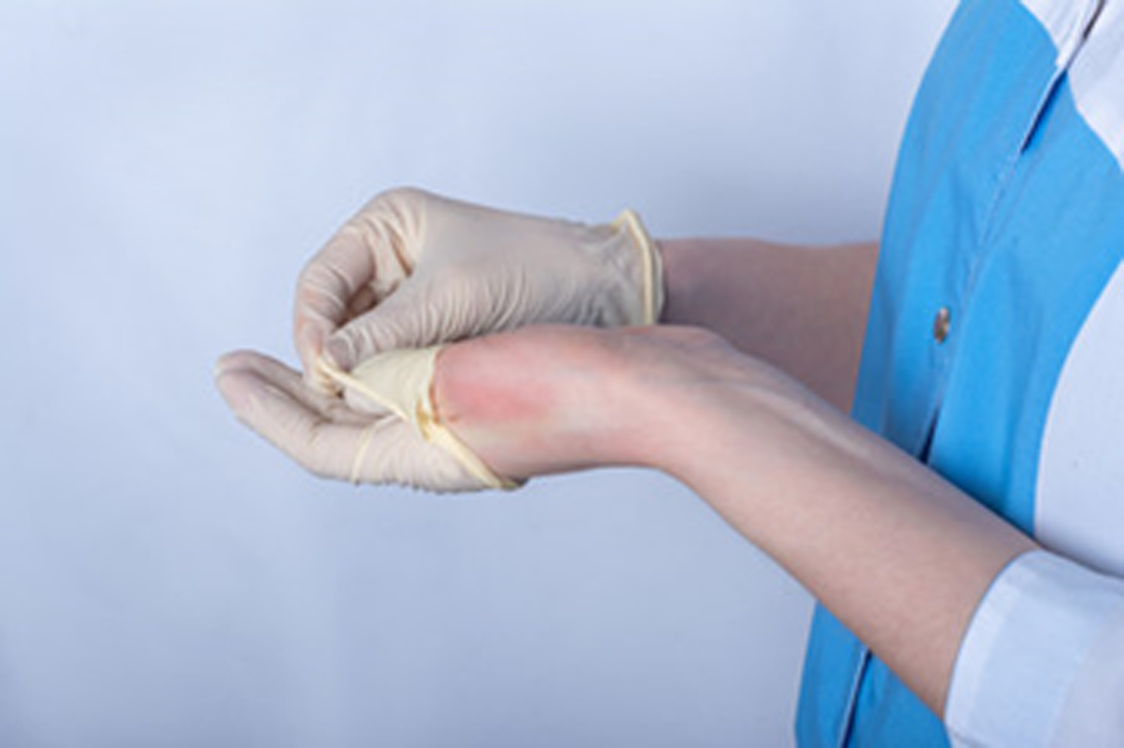 |
Small particles in contact with the outside world, ex. pollen or dust. Common diseases include asthma, hay fever, allergic rhinitis, ectopic dermatitis, and systemic allergic reaction. |
Type II
|
|
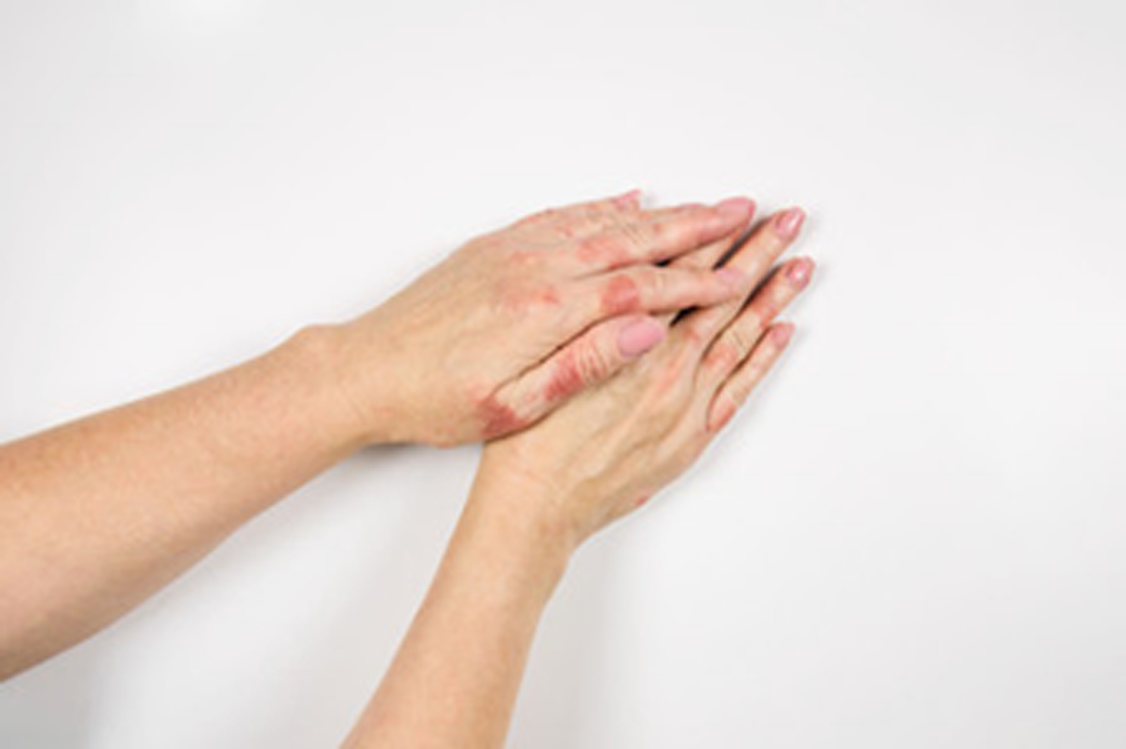 |
Cellular antigen is the hemolytic phenomenon of rejection of different blood groups in specific tissues or cells after blood transfusion. ex. Hemolytic anemia, drug reaction. |
Type III
|
|
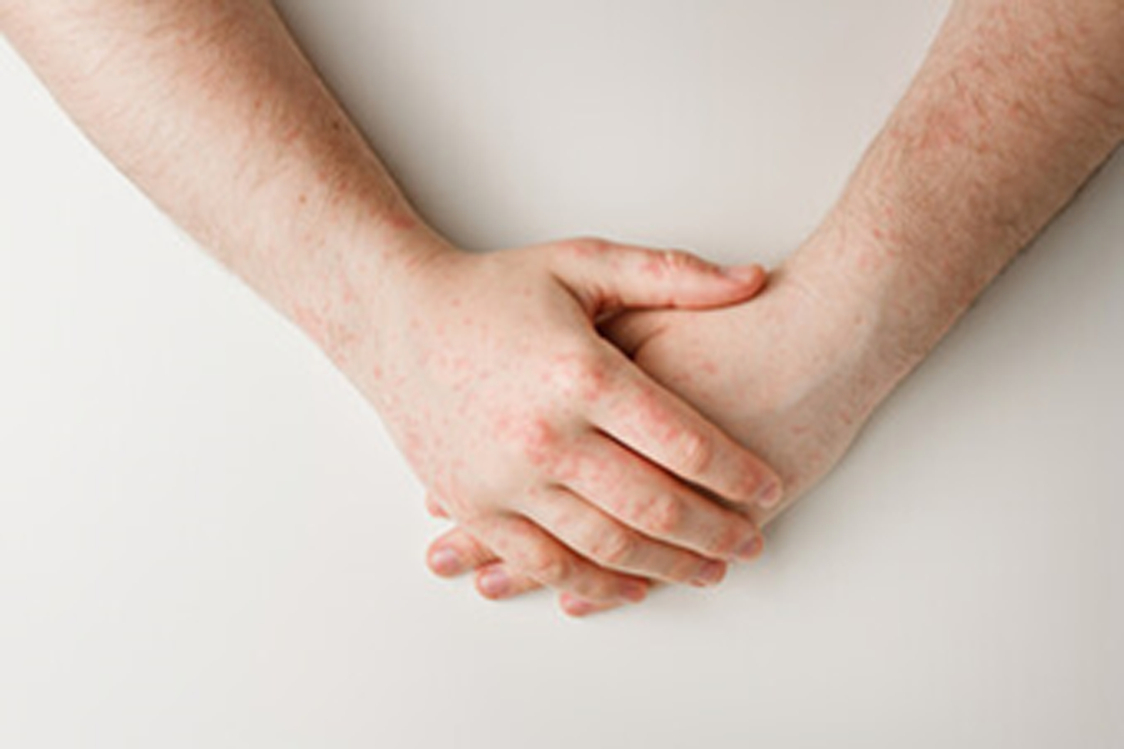 |
Soluble antigen. Common diseases include rheumatoid arthritis, allergic pneumonia, serum disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, etc. |
Type IV
|
|
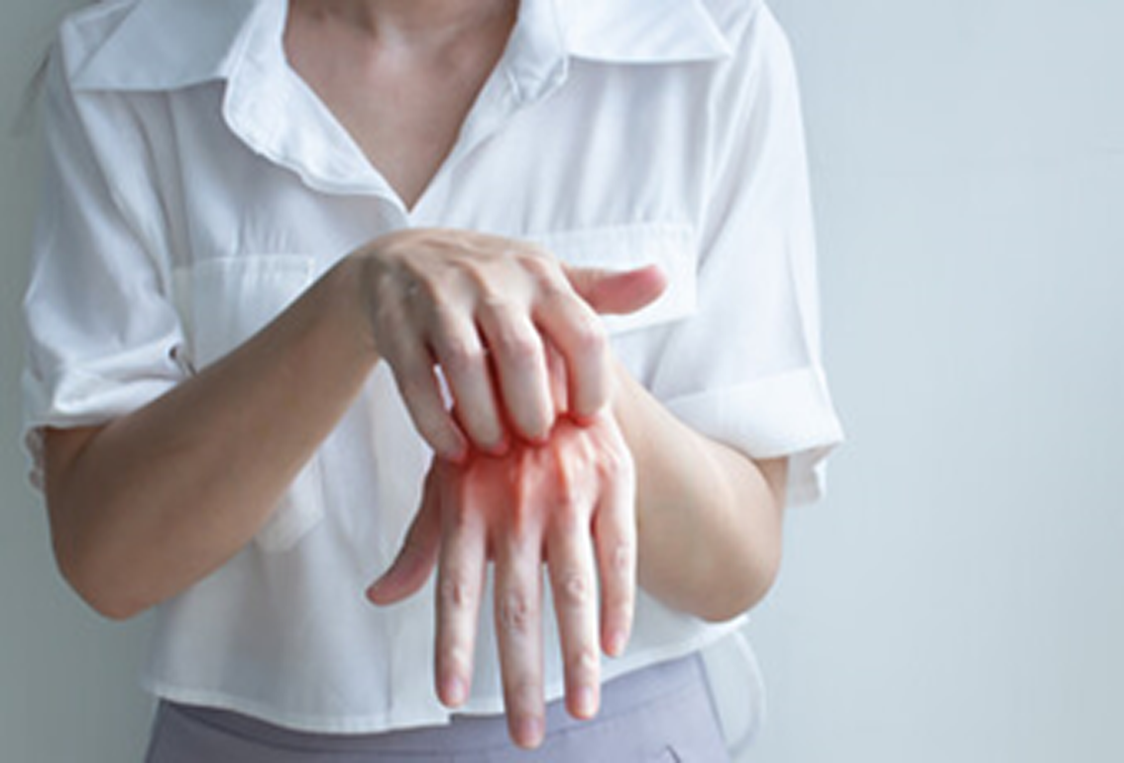 |
Soluble antigens and cellular antigens, such as microorganisms, proteins , plants or drugs. Allergic reactions will not occur immediately, but will occur after 48 ~ 72 hours of skin contact with allergens. |

